By Weiyu Feng, MEng ’22 (EECS)
This op-ed is part of a series from E295: Communications for Engineering Leaders. In this course, Master of Engineering students were challenged to communicate a topic they found interesting to a broad audience of technical and non-technical readers. As an opinion piece, the views shared here are neither an expression of nor endorsed by UC Berkeley or the Fung Institute.
VR games for physical rehabilitation
One of the main aims of VR video games is to facilitate patients’ rehabilitation process. For physical rehabilitations, computer assisted virtual rehabilitation environments and gamification mechanics enable patients to actively perform desired exercises with more fun through VR games compared with traditional methods, leading to a faster rehabilitation process and better performance. Many studies have showed the improvement of patients’ balance, endurance, dexterity, speed, and range of motion after exercising in VR games. For instance, Alicia Cuesta-Gómez recently conducted a comprehensive analysis of using VR game in upper limb rehabilitation and concluded that such an approach not only demonstrated significant improvements for dexterity and coordination in patients, but also resulted in high patients’ satisfactions.VR games for mental rehabilitation
In addition to physical rehabilitations, mental rehabilitations could benefit from the narrative nature of VR video games. By virtually reconstructing selected scenes of certain phobias and manually controlling the environments, doctors could create effective psychotherapies to treat various phobias that traditional treatments can hardly deal with. For example, Vida Kabiri Rahani and his team developed a VR game “Claustrophobia Game” for treatment of claustrophobia. After performing several rounds of user tests, the team analyzed the collected statistical data, and the results demonstrated a significant anxiety decrease of users after they played the game. In addition to phobias, other psychological diseases such as post-traumatic stress disorders, eating disorders, and anxiety disorders could also be effectively treated by using similar methodologies.VR game for pain relief
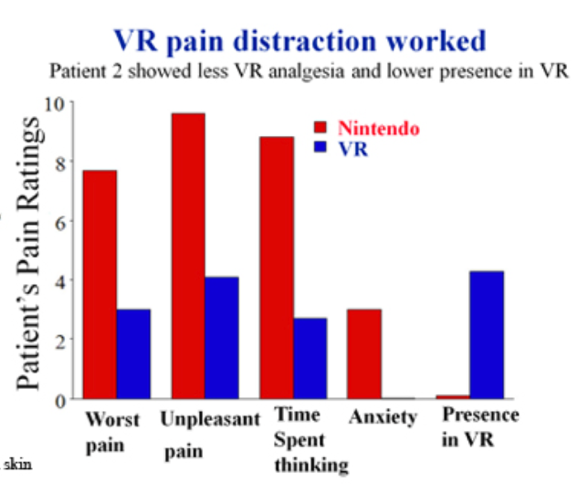
Limitations of applying VR game in clinical
Inevitably, applying VR video games in clinical settings faces various challenges. Recently, some researchers identified these challenges. One of the major challenges is theoretical immaturity. As a novel therapy approach, VR games lack solid theory foundations. Although there are many positive results of applying VR games in clinical settings, researchers still struggle with proposing or proving the mechanics behind the phenomenon, making VR games as an immature therapy that may contain many unknown side effects. Another challenge identified is the lack of technical standards in the current industry. With no agreement on technical standard, the quality and effectiveness of VR game therapy could be a big concern. Other challenges include costs, separating effects of media versus medium, and practical in vivo issues. People are constantly finding new therapies that could bring more benefits toward patients. VR is just one of them. Although researchers have demonstrated various positive effects, VR game as a novel therapy still has a long way to go; but with the diligent efforts of researchers from all over the world, we could possibly see a beautiful future where patients get treated in a fun but effective way.“Although researchers have demonstrated various positive effects, VR game as a novel therapy still has a long way to go; but with the diligent efforts of researchers from all over the world, we could possibly see a beautiful future where patients get treated in a fun but effective way.”
The future of VR game
Despite all limitations and obstacles, VR games see a very promising future in many fields. By virtue of immersive technology, VR games transcend beyond games. With more explorations, VR games could bring changes to a broad scope of healthcare fields including but not limited to physical and mental rehabilitation, 3D environment simulations, and surgical training systems. By keeping an open mind toward VR games, we shall see how VR games shape the future of healthcare together. Connect with Weiyu Feng.References:
- Minhua Ma School of Computing and Information Engineering, et al. “Adaptive Virtual Reality Games for Rehabilitation of Motor Disorders.” Adaptive Virtual Reality Games for Rehabilitation of Motor Disorders | Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction: Ambient Interaction, 1 July 2007, https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/1763296.1763373.
- Cuesta-Gómez, Alicia, et al. “Effects of Virtual Reality Associated with Serious Games for Upper Limb Rehabilitation in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: Randomized Controlled Trial.” Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, BioMed Central, 13 July 2020, https://jneuroengrehab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12984-020-00718-x.
- Rahani, Vida Kabiri, et al. “Claustrophobia Game: Design and Development of a New Virtual Reality Game for Treatment of Claustrophobia.” Journal of Medical Signals and Sensors, Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd, 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6293643/.
- UW Human Photonics Lab. “Virtual Reality Pain Reduction.”, https://depts.washington.edu/hplab/research/virtual-reality/.
- I. Bratosin, I. Păvăloiu, et al. “Pain Relief using Virtual Reality,” 2019 11th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), 2019, pp. 1–4, doi: 10.1109/ECAI46879.2019.9041996.
- Garrett, Bernie, et al. “Virtual Reality Clinical Research: Promises and Challenges.” JMIR Serious Games, JMIR Publications, 17 Oct. 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6231864/.
Op-ed: Virtual reality video games in healthcare was originally published in Berkeley Master of Engineering on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.